Quantum Machine Learning
Disclaimer. I actually know a little of quantum computing, if I am wrong, correct me where possible.
Beginners Guide
If you are a total beginner to this, start here!
- Quantum mechanics
- Machine learning
- Quantum computing with qiskit
- Quantum machine learning
User story

I choose a lazy person to do a hard job. Because a lazy person will find an easy way to do it. Bill Gates
Theory
Quantum mechanics
Some concepts adapted from scientists in the Twentieth Century to describe quantum mechanics include:
- Huygens — light is a wave.
- Einstein — light consists of particles.
They were both right
- Einstein — particles and photons consist of energy.
- Bohr — an atom consists of a small positively charged neucleus with negatively charged electrons orbiting around the nucleus similar to planets orbiting the sun.
- Quantum leap — movement from one discrete energy level to another.
- Quanta — a minimum quantity of energy involved in an interaction.
- Heisenberg uncertainty principle — one cannot assign exact simultaneous values to the position and momentum of a physical system. Rather, these quantities can only be determined with some characteristic “uncertainties” that cannot become arbitrarily small simultaneously.
- Superposition — ability of a quantum system to be in multiple states at the same time until it is measured.
- Entanglement — the quantum states of two or more objects can be described in reference to each other when separated by distance.
- Classical bits — binary data(1’s and 0’s).
- Quantum bit — can exist in both states until measured.
Quantum devices can be used to accelerate machine learning.
For linear algebra we need to encode the data to quantum bits.
Quantum computers will speed up some AI algorithms, enable new AI algorithms and help AI learn new quantum algorithms.
Finding eigenvalues and eigenvectors of large matrices:
One of the methods to perform the classical Principal Component Analysis(PCA) algorithm is to take the eigen value decomposition of a data covariance matrix. However, this is not so efficient in case of high dimensional data.
Quantum PCA of an unknown low-rank density matrix can reveal the quantum eigenvectors associated with the large eigenvalues exponentially faster than a linearly-scaled classical algorithm.
Finding nearest neighbours on a quantum computer:
The quantum algorithms presented here for computing nearest neighbours, that are used in supervised and unsupervised learning, place an upper bound on the number of queries to the input data required to compute distance metrics such as the Euclidean distance and inner product. The best cases show exponential and super-exponential reductions in query complexity and the worst case still shows polynomial reduction in query complexity over the classical analogue.
Machine learning
Machine learning is taking data and finding patterns in the data, e.g., voice recognition listens to what your speak and tries to determine what you are saying and consequently your intentions.
It is still hard to extract patterns from data with our classical computers.
- Supervised
- Support vector machine
- K nearest neighbours
2. Unsupervised
- Clustering
- Principal Component Analysis
3. Deep learning
- Boltzmann machine
So this is just a problem in linear algebra in high vector spaces. There are alot of machine learning algorithms that depend on linear algebra in high dimensional vector spaces.
Methods that lie under the hood for most machine learning algorithms are:
- Fast Fourier transform
- Finding eigen vectors and eigen values
- Matrix inversion
Quantum machine learning
- Automatic Differentiation — Automatically computing derivatives of the steps of computer programs.
- Circuit Ansatz — An ansatz is a basic architecture of a circuit, i.e., a set of gates that act on specific subsystems.
- Differentiable Quantum Programming — The paradigm of making quantum programs differentiable, and thereby trainable. See also quantum gradient.
- Quantum Embedding — Representation of classical data as a quantum state.
- Quantum Gradient — The derivative of a quantum computation with respect to the parameters of a circuit.
- Variational circuit — Variational circuits are quantum algorithms that depend on tunable parameters, and can therefore be optimized.
Vectors are in high dimensional space.
We need to encode data from classical data to quantum mechanical state.
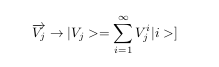
For classical data we have d=2^(2).
For the quantum system we have states which is equal to,
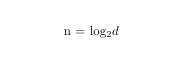
where n is the number of possible states
This means that we have exponentially compressed the data in representation.
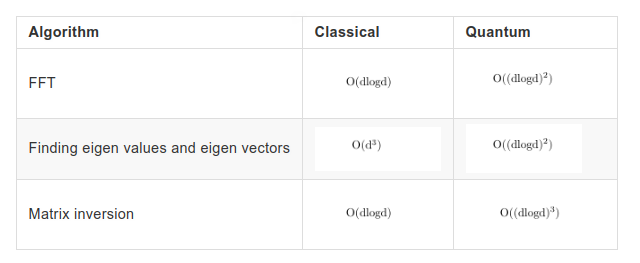
As we can see quantum states have exponentially reduced the number of bits. For classical systems they have many data bits hence they preprocess the data in order to reduce it to fit in a higher dimensional space, e.g., Netflix.
For a terabyte of data we only need to use a circuit with only 40 qubits.
Quantum deep learning doesn’t necessitate faster processes but will necessitate faster linear algebra computations.
qRAM

Quantum computing
Quantum Gates
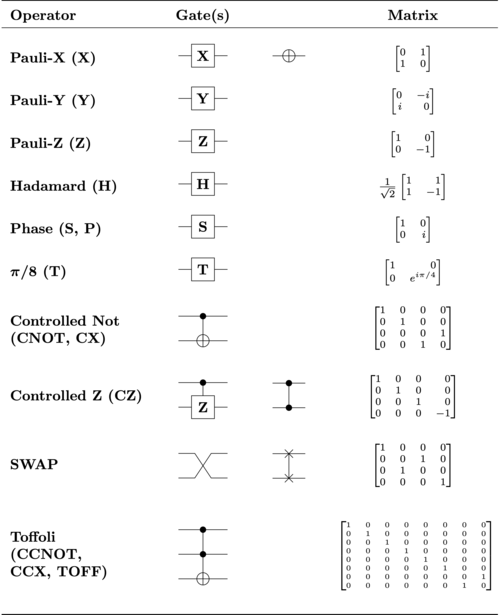
References
Read more about Gherkin here: https://docs.cucumber.io/gherkin/reference/
Awesome quantum machine learning: https://github.com/krishnakumarsekar/awesome-quantum-machine-learning
Appendix and FAQ
Find this document incomplete? Leave an issue or comment!